Waterfalls
The Alternation fashion of rocks from hard to soft is known as waterfalls. Waterfalls are spectacular displays of the beauty and power of nature. The waterfall are caused because of sudden brakes in longitudinal course of the rivers due to a host of factors that are
- Variation in the relative resistance of Rock,
- Relatively difference in topographic reliefs,
- Fall in the sea level and related rejuvenation,
- Earth movement etc.
The
highest waterfall in the world is Angel Falls in Venezuela at a height of over
3000 feet. A fall that descends in a series is referred to as a cascade Gerosoppa (Jog)
waterfall in the Sawarmati River in Karnataka is the highest waterfall in
India.
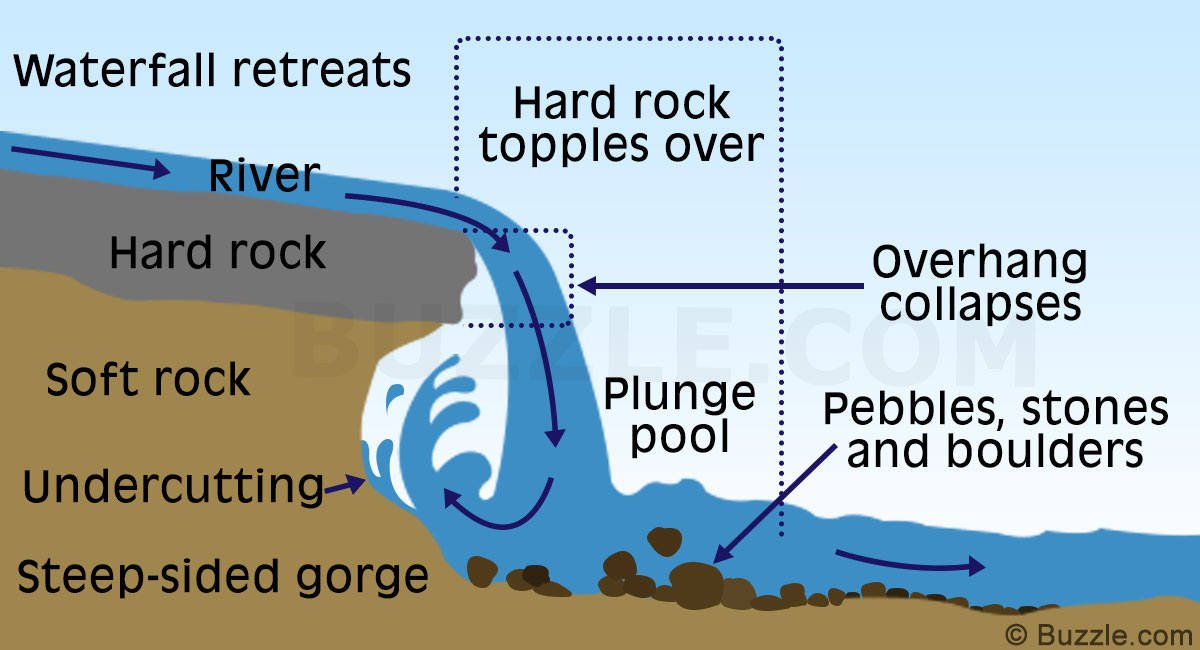
Waterfalls
may at first start off as rapids. The river flows over the hard rock while the
soft rock beneath gets eroded. The erosion of the soft rock occurs more quickly
than the hard rock, and this result in the hard rock being elevated above the
stream bed which sits below. The erosion process of the rocks varies with the
strength and density of the rock and the pace of the flowing river.
Types of waterfalls
- Cascades
Its step like waterfalls.Cascade waterfall especially a series of small falls, consisting of water descending over rocks or boulders. It may be natural or it may be artificial. The cascade has often been used as a feature of formal gardens.
- Canadian waterfalls

The top rock formation was composed
of erosion-resistant limestone and dolodtone. That hard layer of stone
eroded more slowly than the underlying materials. Best example is Niagara
Falls.
- Chute waterfalls
This is formed by vertical erosion and basically goes out from very narrow path. A large quantity of water forced through a narrow, vertical passage is known as chute waterfalls.
- Horsetails waterfalls

Descending water maintains contact with bedrock most of the time (e.g. Jog Falls).
- Twin pool waterfalls

Twin Falls was a waterfall that was so named because it used to have two side-by-side plunges at a split.
Note
Niagara Falls was formed
when glaciers receded at the end of the Wisconsin glaciations (the last ice
age).




